General Guidelines
Desktop/Web
- Browser Support
- Windows
- Installers
- Consoles
- Dashboards
- Workspaces
- Navigation
- Forms
- Validation
- Error Messages
- Labels/Required Fields
- href="forms-inline-messaging.php">Inline Messaging
- Edit in Place
- Status/Progress Indicators
- Tab Indexes
- Input Prompts
- Selection
- Disabled Fields
- Structured Format
- Search
- Grids/Tables
- Dialog Boxes
- Modals
- SuperBox
- Wizards
- Messages
- Progressive Disclosure
- UI Controls
- UI Text (IDD)
- Data Visualization
Mobile (Tablet & Phone)
- Resolutions
- Gestures
- Touch
- UI Controls
- Buttons
- Check Boxes
- Color Picker
- Date Picker/Calendar
- Drop Down List
- Combo Box
- Groups and Separators
- Links
- List Boxes
- Progress Indicators
- Radio Buttons
- Scrollbars
- Sliders
- href="mobile-snap-drag-controls.php">Snap-Drag Controls
- Spin Controls
- Status Indicators
- Text Boxes
- Toolbars
- Screen Orientation
- Page Composition
- Display of Information
- Control and Confirmation
- Revealing More
- Widgets
- Input and Output
- Input Method Indicator
- Autocomplete and Prediction
- href="mobile-directional-entry.php">Directional Entry
- Press and Hold
- Focus and Cursors
- Input Areas
- Form Selections
- Mechanical Style Controls
- Clear Entry
- Tones
- Voice Input
- Voice Readback
- Voice Notifications
- Haptic Output
Visual Design Guidelines
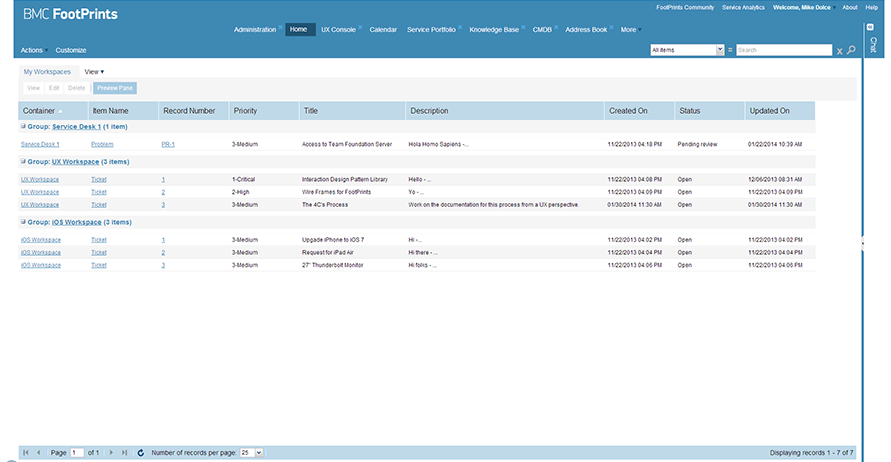
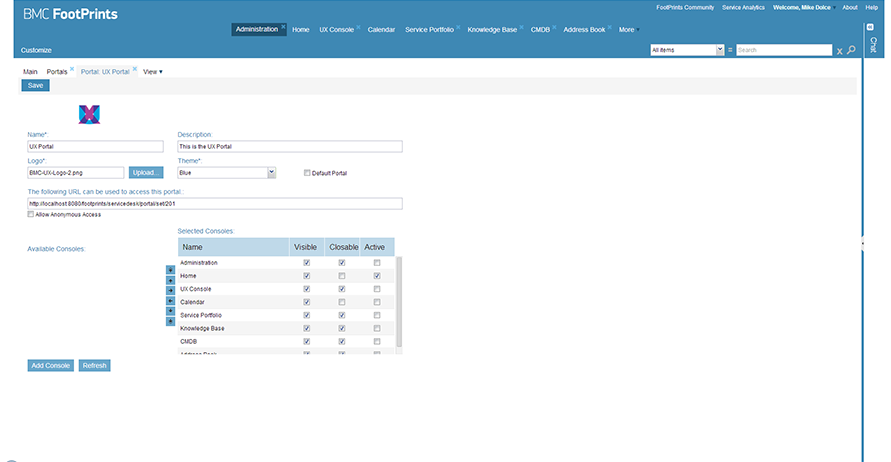
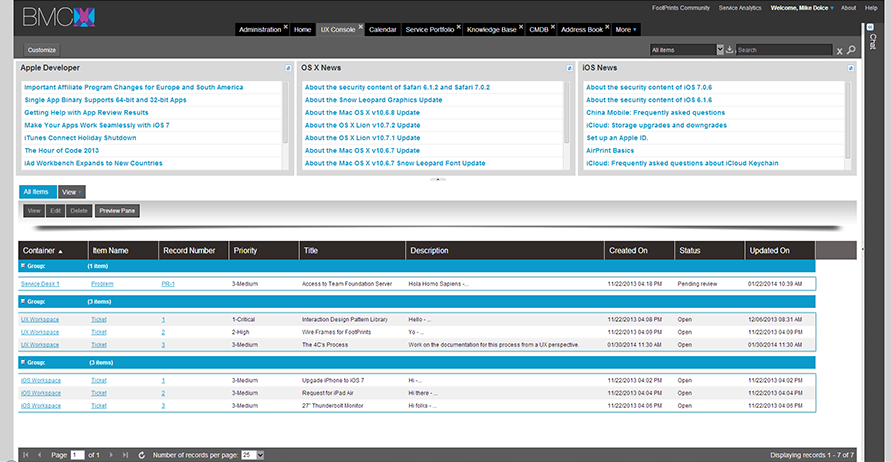
Consoles - Portals
Problem
Users want to access a wide variety of information - and users have a need to define their own page elements.
Solution
Create a Portal - a web system that provides the functions and features to authenticate and identify the users, and also provides them with an easy, intuitive, personalized and user-customizable web-interface for facilitating access to information and services that are of primary relevance and interests to the users.
Key features of portals
- Security
- Access different data
- Transactions
- Search
- Publish Content
- Personal Content
What a portal does:
- Enables universal login
- Handles both structured and unstructured data
- Facilitates multi-channel consistency
- Facilitates messaging and notification
- Automated tuning: pervasive content can be tuned based on personalization, location, browser, etc.
- Integration to other systems
What a portal is not:
- It is not just a Website (which is usually characterized by static information)
- It is not just a personalized intranet
- It is not just a personalized extranet
- It is not just a personalized front end for business applications
- It is not just groupware
- It is not just a personalized knowledge management solution
- It is not just a sophisticated search engine
- Instead, a portal is nothing less than just one personalizable, browser based user interface to all the components mentioned above.
Variations
An enterprise portal (sometimes called a corporate portal) provides personalised access to an appropriate range of information about a particular company.
A workspace portal is a single, coherent, integrated portal that presents its users with all the information they need to carry out their jobs.
Knowledge portals increase the effectiveness of knowledge workers by providing easy access to information that is necessary or helpful to them in one or more specific roles.
How
First log in and then present a customized personal section, which will serve as the home page for the user. The page is built using 'modules' that the user has selected. Each module is a Customizable Window. Users can change which modules they want and in which layout and graphical presentation.
The home-page's main function is to guide people to one of the sub-sites. Use "preview blocks" that show what is going on in the specific sub-sites. The home-page generally has a feature article and a list of headlines. Additional common items may include:
- Sub-site navigation
- Logo
- Main navigation and main content
- Right column for contextual or shared content
Use When
The idea of a portal is to collect information from different sources and create a single point of access to information - a library of categorized and personalized content. It is very much the idea of a personalized filter into and application, or a series of applications.
A portal is most often one view in an application which brings information together from diverse sources in a uniform way. Usually, each information source gets its dedicated area on the page for displaying information; often, the user can configure which ones to display. Variants of portals include Mashup (web application hybrid) and intranet "dashboards" for executives and managers. The extent to which content is displayed in a "uniform way" may depend on the intended user and the intended purpose, as well as the diversity of the content. The role of the user in an organization may determine which content can be added to the portal or deleted from the portal configuration.
A portal may use a search engine API to permit users to search application content. Apart from this common search feature, portals may offer other services such as e-mail, news and information from databases. Portals provide a way for enterprises and organizations to provide a consistent look and feel with access control and procedures for multiple applications and databases, which otherwise would have been different web entities at various URLs. The features available may be restricted by whether access is by an authorized and authenticated user (employee, member) or an anonymous site visitor.
Personalization
Personalization is vital to the delivery of appropriate information to portal users: each user gets only the information which is specifically tailored to his/her needs. Personalization should be based on user roles, as well as user preferences.
Types of personalization:
- Personalization of Navigation - e.g. shortcuts to specific information, mostly known as bookmarks or favorites
- Personalization of Data/Content - e.g. which stocks do I want to see in my stock ticker
- Personalization of Layout - e.g., what information appears, where it is located on the screen, in which format, color or size, etc.
An important high-level distinction exists between:
- Design Personalization - the initial appearance of the portal, which may be 'pre-personalized' according to the user's role
- Voluntary personalization - where the user is offered a menu of personalization options to choose from
- Involuntary personalization - where the system itself unilaterally makes decisions for the user according to 'guesses' about user preferences
- Notification
Examples